Protecting a structure from moisture is a critical part of any construction, especially below grade. There are two levels defined by building codes to protect a structure from water. Dampproofing protects a basement or other enclosed space from moisture found in the soil around a home. Impermeable in most instances, it may not protect against a column of liquid water. Waterproofing systems will protect a basement or other enclosed space from liquid water as well as the moisture commonly found in soils. Building codes require any walls below grade with an interior enclosed space that is habitable to have appropriate moisture control. There are many waterproofing systems to choose from and several of these are widely used and perform exceptionally well.
In many installations, a combination of materials offers the best waterproofing performance. The primary methods of waterproofing are: peel and stick membranes; liquid systems that are sprayed, rolled, or applied with a trowel; and dimpled drainage mats which are mechanically fastened to ICF walls. Spray-on membranes for ICF are beginning to grow in popularity, but are dependent on the regional availability
of applicators.
When installing waterproofing or dampproofing, the applicator should ensure that no untreated penetrations are present in the barrier. Failures of the barrier could occur due to fastener placement, rips or tears that are not properly sealed, or an incomplete seal at seams.
Waterproofing ICFs
Waterproofing is a multi-step project, involving many areas of the ICF wall and other building components. Moisture control begins with flashing at the roof line, parging at grade level, membranes below grade, air gap barriers and foundation and site drainage to route water away from the structure. This includes water shed from the structure and runoff from other sources on the property.
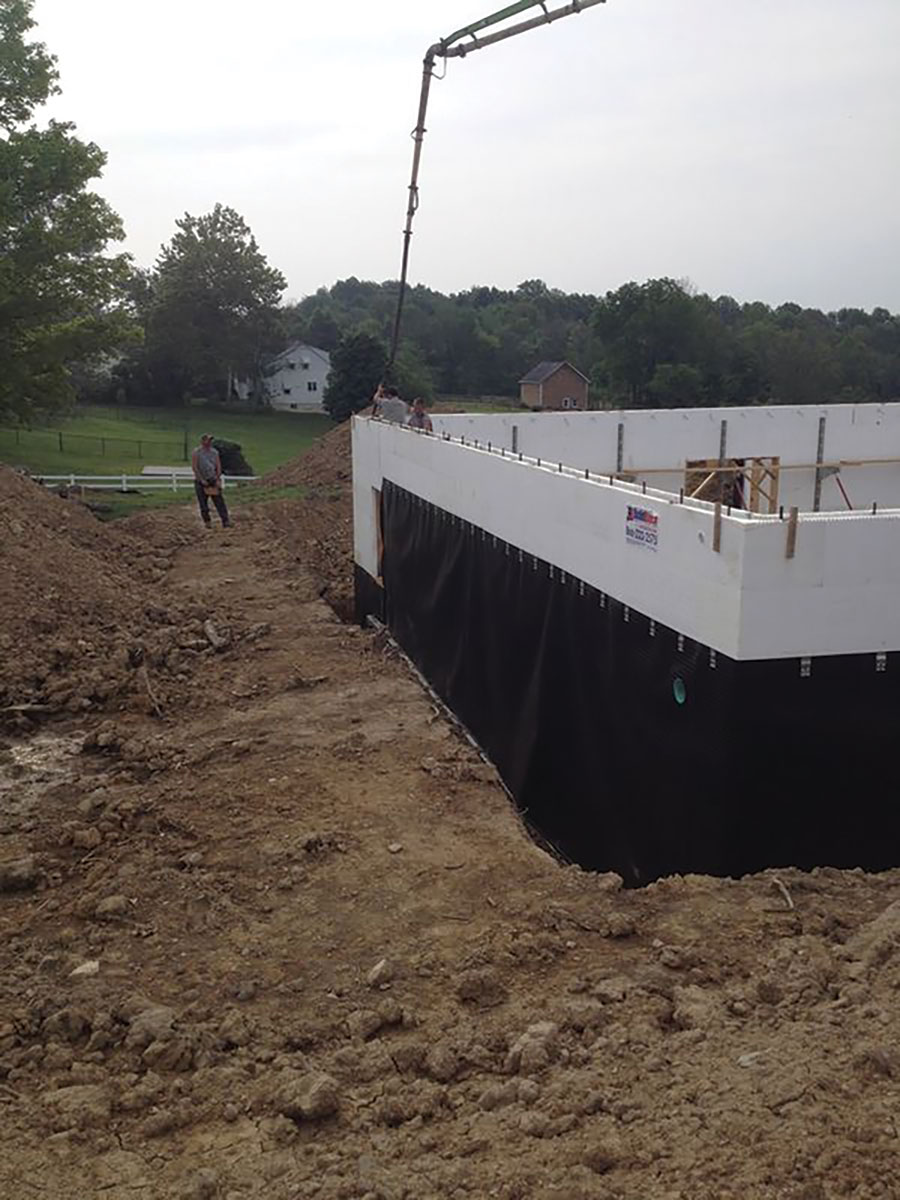
A typical basement will have much of the wall square footage backfilled. This backfill will contain moisture and will apply hydrostatic pressure against the wall. Any moisture or liquid water will seek out cracks or voids, and use them to migrate into your basement. Careful attention to waterproofing will ensure that your structure is dry, comfortable, and energy-efficient.
Waterproofing an ICF structure is substantially different from standard concrete construction. While it is important to place a barrier between the elements and the interior of the home, the nature of that barrier is much more important when working with ICFs.
Due to the nature of EPS foam and its susceptibility to solvents, only water-based materials should be used. A peel-and-stick membrane may also be used with ICFs to maintain a consistent membrane thickness, bridge any gaps or seams, and facilitate easy installation and cleanup.
A combination of waterproofing materials and systems to adequately manage the different factors influencing moisture and hydrostatic pressure in the soil is recommended. Each of these systems provides a different function and complements the other.
Peel-And-Stick Waterproofing Membranes
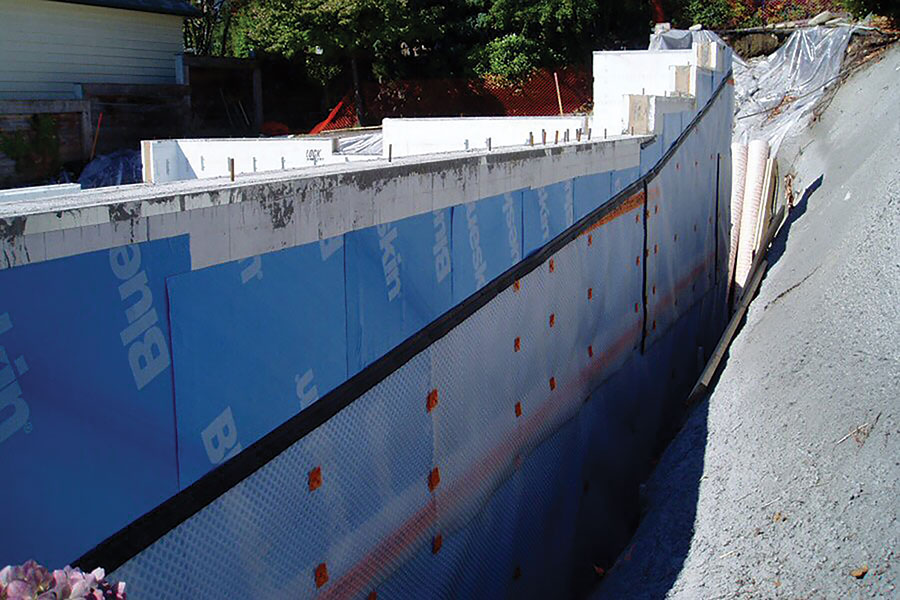
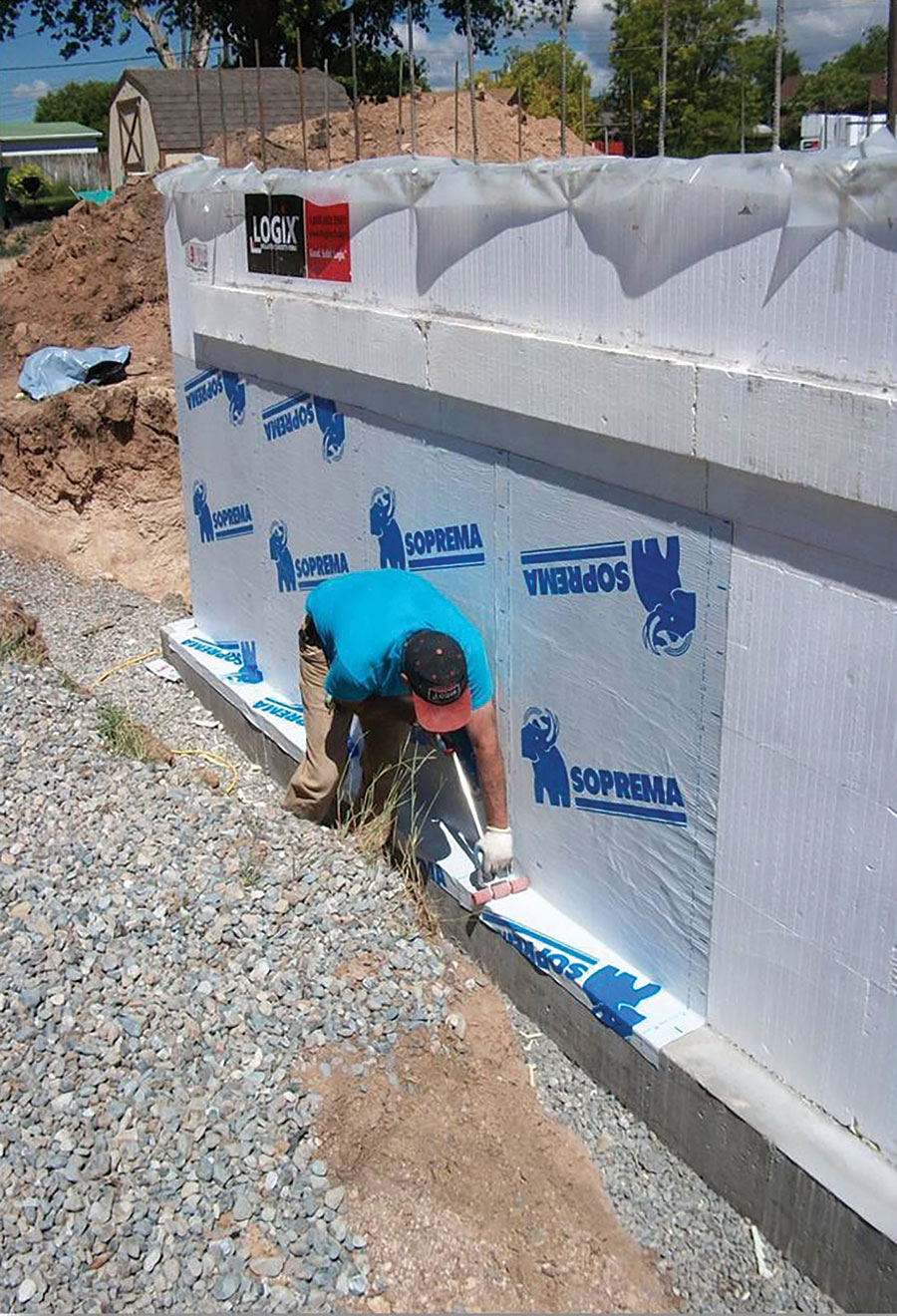
A peel-and-stick waterproofing membrane provides a positive seal against the wall and acts as a barrier to prevent liquid water or water vapor from finding a way into the basement. A flexible self-adhering rubberized asphalt sheet waterproofing membrane is well suited for below-grade waterproofing ICF forms. It is typically 1.5mm (60 mils) thick and is supplied in 100-cm-wide (39-3/8”) rolls. A water-based primer should be used to enhance the bond with the EPS foam.
General ICF Waterproofing Options
- Self-adhesive membrane. This is typically 60 mils in thickness and is often used in conjunction with an air gap or dimpled membrane that protects the membrane from backfill and provides additional hydrostatic pressure relief.
- An ICF compatible spray-on membrane. (Caution: Do not use a petroleum based paint or primer. These products will dissolve the EPS foam.)
- A one-step dimpled plastic mat type protection that provides an air gap between the ICF wall and the surrounding earth.
Causes of Hydrostatic Pressure in Soil
- Proximity to a body of
water. Lakes, rivers, oceans, artesian wells, and underground streams all affect the water table. - Precipitation, including the amount of rain or snow melt both locally and upstream of the site can increase the hydrostatic pressure against a basement.
- Different types of soil have different properties when relating to retention of groundwater.
- Locally heavy rains can saturate the soil and overwhelm its ability to soak up the water increasing fluid pressure on the walls.
Air Gap Membranes
An air gap membrane or dimpled membrane is a plastic membrane with raised flat tabs on one side. The membrane is installed vertically with the raised tabs placed against the wall creating a uniform space between the wall and the membrane. As hydrostatic pressure increases, air is displaced relieving pressure against a basement or foundation. This membrane also provides a clear drainage plane against the wall.
Other Waterproofing Options
Other systems available include rolled, troweled, and sprayed coatings. It is important to note that solvent-based coatings will dissolve the foam. Some coatings may do so slowly, and it may go unnoticed until after back-
filling. Without the foam to support the coating, the waterproofing loses its effectiveness. Test these products on EPS prior to application.
Waterproofing Concrete Additives
Concrete additives that provide integral crystalline waterproofing are available from a variety of companies. The active ingredient, crystalline silica and the hydrated compounds in the concrete react in the presence of water. An insoluble crystal grows into the void, toward the water source, effectively sealing cracks and fissures in the concrete.
These additives are best used to prevent water wicking into the concrete core or should water enter the wall cavity. Concrete may form small capillaries that would allow water to travel through the wall. This type of water infiltration is difficult to detect as the entry and exit of the moisture may be far apart. These materials also increase the compressive strength of the concrete and provide a water resistant buffer protecting rebar from moisture and corrosion.
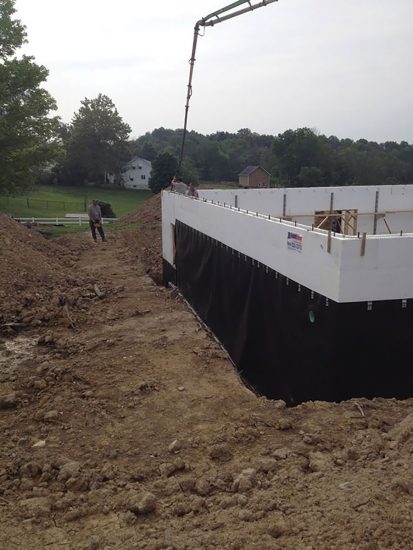

Dimple sheets provide an excellent drainage plane, and also serve as protection during backfill operations.
Footing or Base Drainage Systems
Adequate drainage around the footings or base is necessary to maintain a dry basement. Several methods are used for perimeter drains including drain tiles, corrugated pipe and specialty drain products. Stay-in-place footing forming systems interconnect a drain on the inside and outside of the footing. This drain connects to a sump or daylight drain and can also be designed to evacuate radon gas from foundations through passive or active venting. Many codes are shifting toward active venting. If used with passive venting and a sump, the sump must be sealed and tested to prevent radon gas from entering through the drainage system.
Below Grade Moisture Control
Proper backfilling around below-grade walls requires more than replacing and compacting soil around the walls. Backfill materials should be free from large inclusions, such as stones, sticks, or other large debris. These can damage the waterproofing. If the waterproofing is damaged it may require the backfill to be removed and sections of waterproofing replaced at great cost.
Once the entire wall has been waterproofed layer, it should be backfilled correctly. The correct type of material should be placed in the proper location
and compacted as specified. Fine gravel should be placed to the height of at least 12-inches at the base around the drain pipe or stay in place forming system. A layer of silt cloth should then be placed on top of the gravel before additional backfill is placed. Backfilling can only occur after the walls are poured and floor trusses are in place to help support the walls from pressure of the backfill.
Backfill and compaction must be done carefully to prevent waterproofing from being pulled loose from the walls. Backfill material should then be built up around the basement or stem/frost walls until it is higher than the surrounding grade, and sloping smoothly away from the home or building, ensuring standing water drains away from foundation walls.
Above Grade Moisture Control
EPS foam is considered a Class 2 Vapor Retarder. It reduces the transmission of moisture and water vapor through the material. The concrete core likewise offers protection against water vapor, when installed properly, with a well-drained footing, and appropriate waterproofing and dampproofing.
Air Barriers may be any number of materials or coatings used to slow or eliminate air infiltration. ICFs typically do not need a whole wall air barrier, as the concrete core serves as a very effective air barrier. To meet some standards (LEED, Passivhaus, Net-Zero, and others), it may be necessary to add an air barrier at windows and doors, sealing the bucking to the wall and the window or door frame to the bucking.
Independent testing in accordance with ASTM E283 concluded an ICF wall assembly with a six-inch concrete core has negligible air infiltration and therefore the wall assembly acts as an air barrier itself. No additional materials are required to be installed over ICF forms for the wall system to act as an air barrier.
Moisture Control Around Windows and Doors
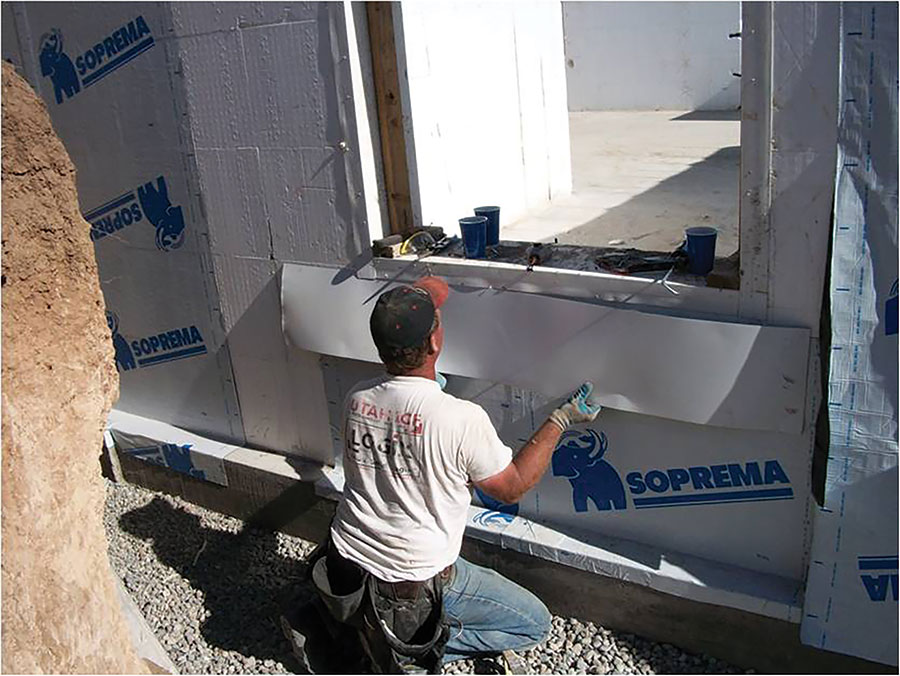
Bucking is the process of using a wood, steel, vinyl, or EPS forming material to create openings in an ICF wall. They also serve as anchors or attachment points for windows and doors. Waterproofing openings typically consists of applying external flashing, such as peel-and-stick materials or HVAC tape covering the bucking material and framing.
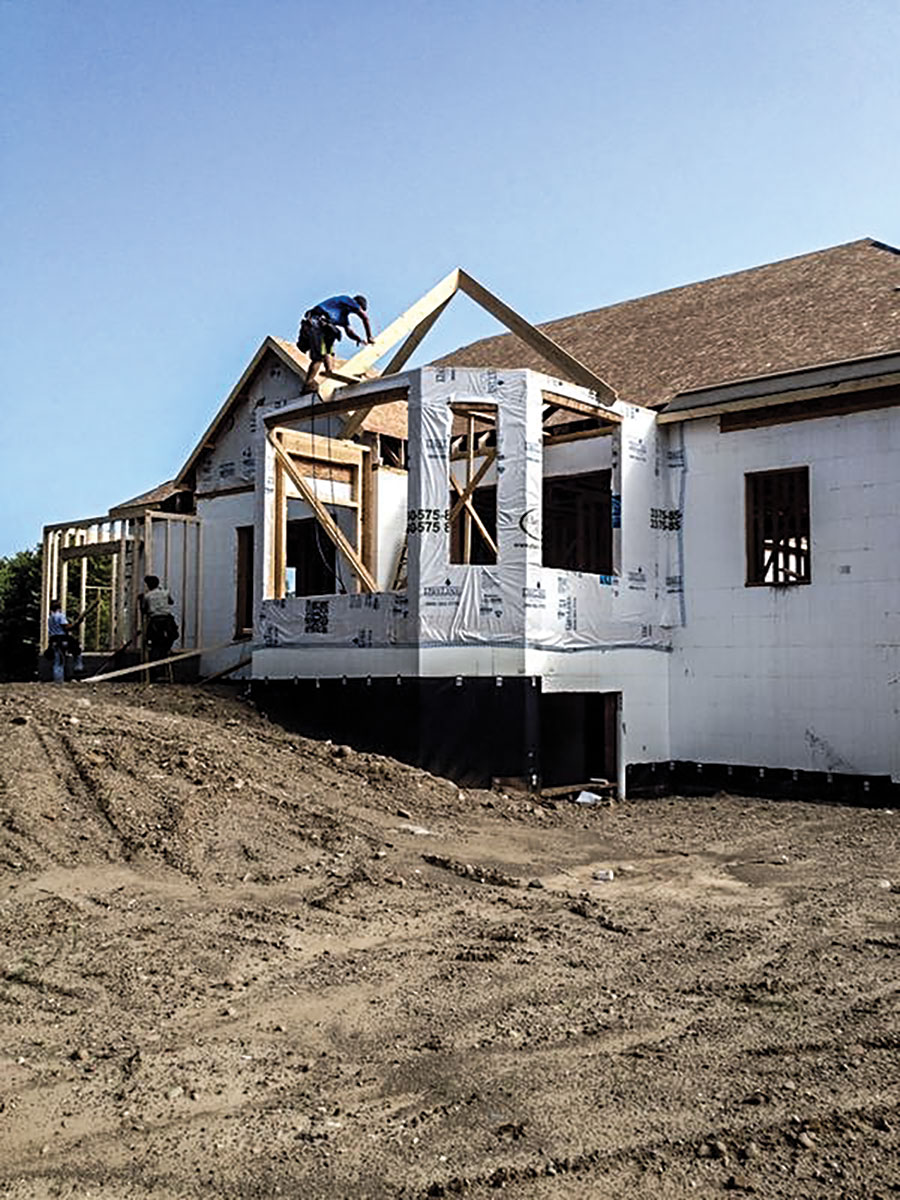

Housewraps are not needed on ICF walls, but may be necessary on framed portions, such as gables, dormers, and window walls.
Flashing is used in many areas of an ICF installation and is intended to direct the flow of liquid water away from moisture sensitive materials and away from the interior of the home. It should always extend past the layer below it, much like shingles in a roof continuously overlap. Window and door flashing performs the double duty of flashing against moisture and air infiltration.
Flashing should be installed at the top of a wall, around doors and windows, and at the base of walls where water may be present at a cold joint. Flashing may also be used below brick or exterior finishes to direct water outside of the walls structural layers.
Conclusion
There are many proven options to prevent moisture or liquid water through an ICF wall below or above grade. Placing the appropriate barrier to moisture is critical to ensuring the ICF walls perform to their highest level. The specific combination of materials for use in your project will vary based on local conditions and manufacturer recommendations. Design and build your structure right from the start and prevent lingering problems caused by cutting corners, skimping on materials, or improper installation. Many manufacturers recommended that all below grade crawlspaces or basements be waterproofed even if not used as a living space. Consult local codes and choose the solution that will provide the best below grade protection for the life of the structure.
Brian Corder is the president of sales and marketing for BuildBlock Building Systems. This article is based on the BuildBlock Comprehensive Guide to ICF Waterproofing and was prepared in collaboration with Insulating Concrete Forms Manufacturers Association (ICFMA) members.
Basement and Crawlspace Waterproofing Requirements
The International Residential Code Section R406 specifies that, “Foundation walls that retain earth and enclose interior spaces and floors below grade shall be dampproofed from the top of the footing to the finished grade.” Additionally, “In areas where a high water table or other severe soil-water conditions are known to exist, exterior
foundation walls that retain earth and enclose interior spaces and floors below grade shall be waterproofed from the top of the footing
to the finished grade.”
Crawlspace requirements vary by the type and use of the crawlspace and local codes. Stem or frost walls that have fill against both sides do not typically need to be waterproofed.














Great article! How would a dimple mat be fastened over ICF?
Nearly always, its mechanically attached (nailed or screwed to the webs of the ICF form). Dimple mat on ICF is common enough that each manufacturer has their own recommendations. Many brands use a termination strip at the top of the wall (at grade) and around windows to prevent infiltration at these critical points
I’m trying to find a detail which diagrams the assembly of an ICF roof deck illustrating the layers of waterproofing. I’ve contacted a few mfgs of concrete waterproofing products and have been told that they don’t warrant their product on an ICF roof deck. Any ideas?
The major foam decking manufacturers, including LiteDeck and Insul-Deck, have details available. Contact their respective technical departments for additional information.
In just install icf fox blocks looking for membrane what is the best out there for I C F blocks
“Hello Rene,
We at DMX Plastics Limited manufacture dimpled membranes that are also suitable for ICF foundations. DMX AG Foundation Wrap can be installed with ICF foundations. Our foundation wrap, when purchased in-store or online at Menards, or through special order at Home Depot, includes the following accessories: DMX Washers and DMX Flextrim (mold strips).
Please make sure to use 1 ½” deck or drywall screws instead of concrete nails. The screws are to be anchored into the cross webs locations based on the diagram above. Please refer to our installation manual, available on our website http://www.dmxmembranes.com, for further details regarding the installation of DMX AG with ICF foundations.
Feel free to contact customer service at 1-855-501-7837 (Toll Free) regarding any further questions.”
Customer Care – DMX Plastics Limited
Customerservice@dmxmembranes.com
http://www.dmxmmembranes.com
Thank you.
Best regards,
Joanna Vennik
Hey, just found this. Great article with lots of info. Question, what do you recommend in very cold climates? THanks